Diabetes is widely known for affecting blood sugar levels, but many people are unaware that it can also seriously impact vision. One of the most common and potentially sight-threatening complications of diabetes is diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of preventable blindness among adults.
Understanding diabetic eye disease, recognizing early symptoms, and seeking timely diabetic retinopathy treatment can make a significant difference in preserving your vision.
The good news? With proper diabetes eye care, vision loss is largely preventable.
Let’s explore how diabetes affects your eyes and what proactive steps you can take.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
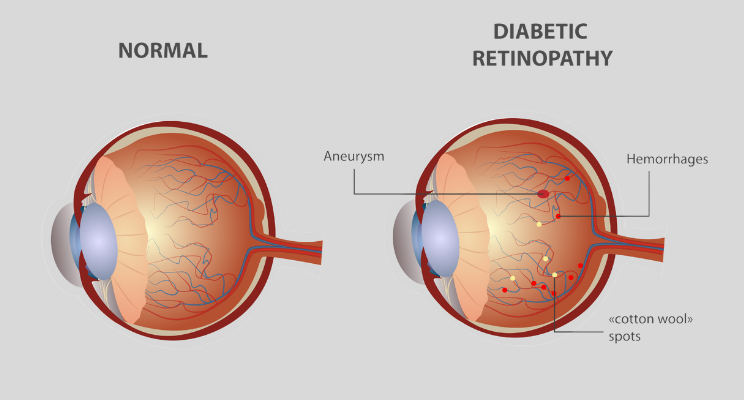
Diabetic retinopathy is a type of diabetic eye disease that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye responsible for clear vision.
High blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina. Over time, these vessels may:
- Swell and leak fluid
- Close off completely
- Grow abnormally (advanced stages)
When left untreated, this damage can lead to blurred vision, retinal swelling (macular edema), and even permanent blindness.
How Diabetes Affects Your Vision
Diabetes impacts vision gradually. In the early stages, symptoms may be mild or even absent. However, as the condition progresses, patients may experience:
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Dark spots or floaters
- Impaired color perception
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Sudden vision loss in severe cases
Because early diabetic eye disease often develops without noticeable symptoms, regular screening becomes critical.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Understanding the stages helps highlight the importance of early diagnosis and diabetic retinopathy treatment.
1. Mild Non-Proliferative Stage
Small areas of balloon-like swelling (microaneurysms) appear in retinal blood vessels. Vision may still be unaffected.
2. Moderate to Severe Non-Proliferative Stage
Blood vessels begin to block, reducing oxygen supply to the retina.
3. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
In advanced cases, new abnormal blood vessels grow. These vessels are fragile and may bleed into the eye, causing serious vision loss.
Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Who Is at Risk?
You are at a higher risk of developing diabetic eye disease if you:
- Have had diabetes for many years
- Poorly manage blood sugar levels
- Have high blood pressure
- Have high cholesterol
- Are you pregnant with diabetes
The longer you live with uncontrolled diabetes, the greater the risk to your eyes.
The Importance of Regular Diabetes Eye Care
Comprehensive eye examinations are essential, even if your vision seems fine.
Annual dilated eye exams allow specialists to detect early changes in the retina before symptoms appear. Timely diagnosis ensures intervention before irreversible damage occurs.
Diabetes eye care should be considered a routine part of diabetes management, just like monitoring blood sugar or blood pressure.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Options
The good news is that modern medicine offers effective diabetic retinopathy treatment options, especially when the condition is diagnosed early.
✔ Blood Sugar & Blood Pressure Control
Managing diabetes effectively is the first line of defense. Stable blood sugar slows disease progression.
✔ Laser Therapy
Laser treatment helps seal leaking blood vessels and prevent abnormal vessel growth.
✔ Anti-VEGF Injections
These medications reduce abnormal blood vessel formation and swelling in the retina.
✔ Vitrectomy Surgery
In advanced cases with bleeding inside the eye, surgery may be required to remove blood and scar tissue.
Treatment plans vary depending on the stage of diabetic eye disease, which is why personalized evaluation is essential.
Can Diabetic Retinopathy Be Prevented?
While diabetic retinopathy cannot always be completely prevented, its progression can be significantly slowed with proper care.
Here’s what you can do:
- Maintain optimal blood sugar levels
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol
- Follow a diabetes-friendly diet
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking
- Schedule regular eye screenings
Consistent diabetes eye care dramatically reduces the risk of vision-threatening complications.
When Should You See an Eye Specialist?
Seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
- Sudden vision changes
- New floaters
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Dark areas in your field of vision
Even without symptoms, yearly eye examinations are non-negotiable for individuals with diabetes.
Expert Care Matters
Managing diabetic eye disease requires experience, precision, and advanced diagnostic technology. At Eyecure Hospital, patients receive comprehensive diabetes eye care with modern imaging systems, early detection protocols, and advanced diabetic retinopathy treatment options tailored to each individual’s needs.
The goal is simple: early diagnosis, effective intervention, and long-term vision preservation.
Protect Your Sight Before It’s Too Late
Diabetic retinopathy often develops silently, but its consequences can be life-altering. The key to prevention lies in awareness, routine screening, and timely treatment.
If you or a loved one lives with diabetes, don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Prioritize regular eye exams and proactive diabetes eye care, because preserving your vision is preserving your independence and quality of life.
Your eyes deserve attention. And with the right care, vision loss from diabetic retinopathy is largely preventable.